Build Your Project
Create your first AI SCADA project from scratch.
Understanding the Editor Interface
Project Manager
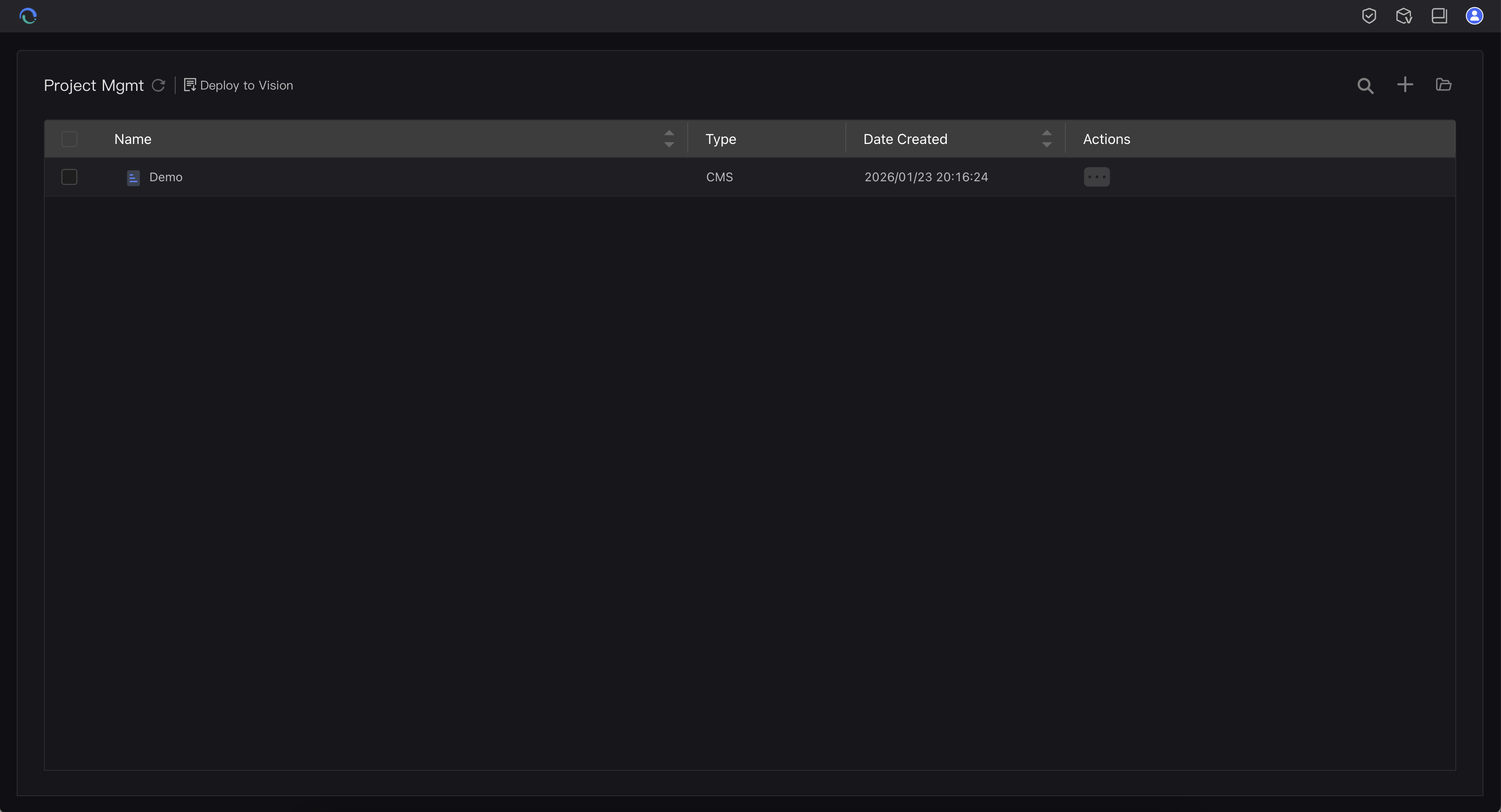
The first screen you see when launching AI SCADA Editor:
- Create New Project - Click "New Project" to start fresh
- Open Existing Project - Double-click a project record to enter the development environment
- Manage Projects - Backup, restore, import, and export projects
- View Project Info - Project name, creation time, last modified time
Editor Main Interface
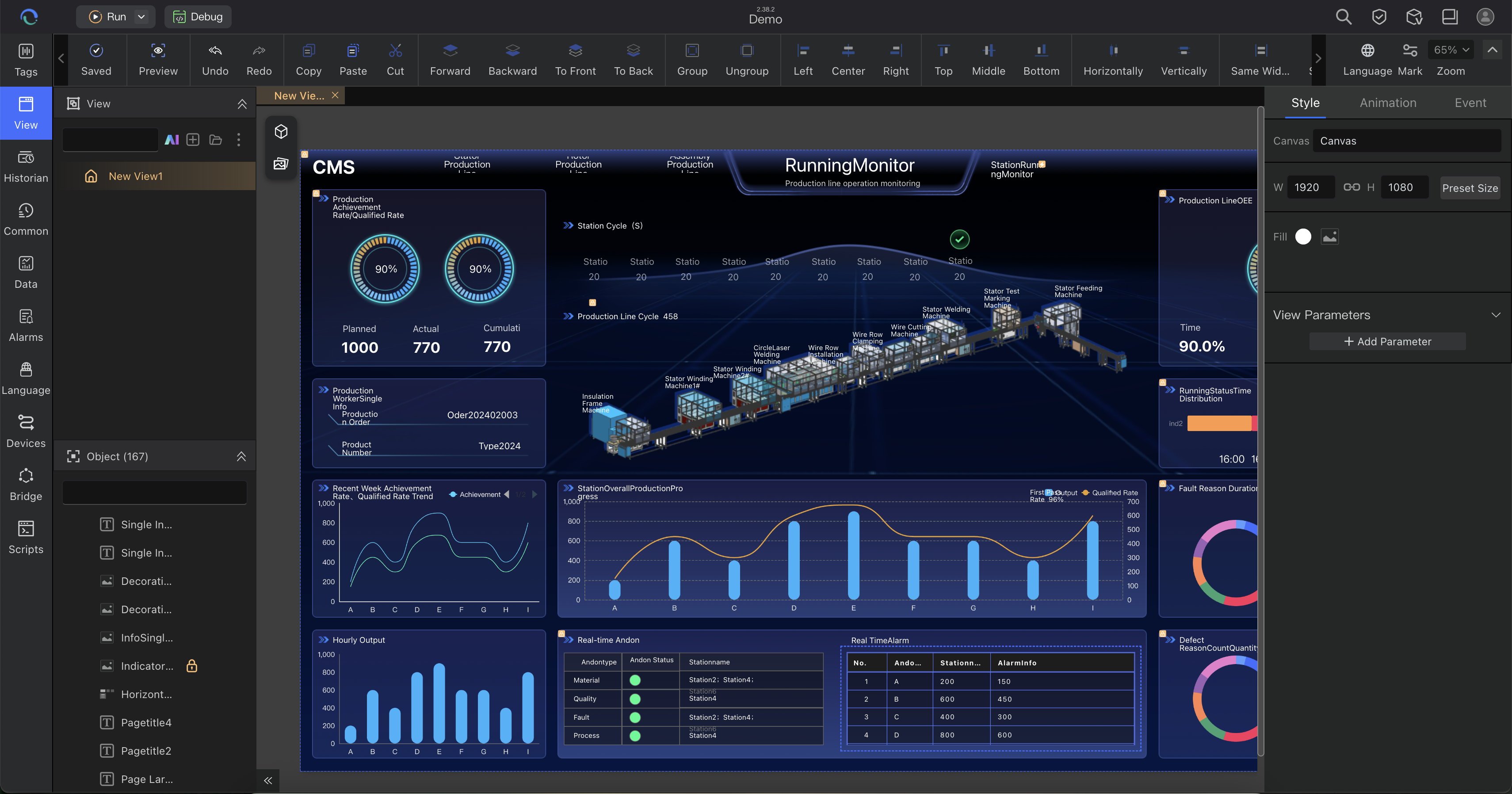
The main interface layout after entering a project:
- Top Toolbar - Preview, run, debug, project search, licensing, version notes, help documentation
- Left Navigation - Quick access to different functional views
- Center Workspace - Main editing and configuration area
- Right Properties Panel - Detailed properties of selected objects
Key Functional Views
Tag View - Configure device connections and data points
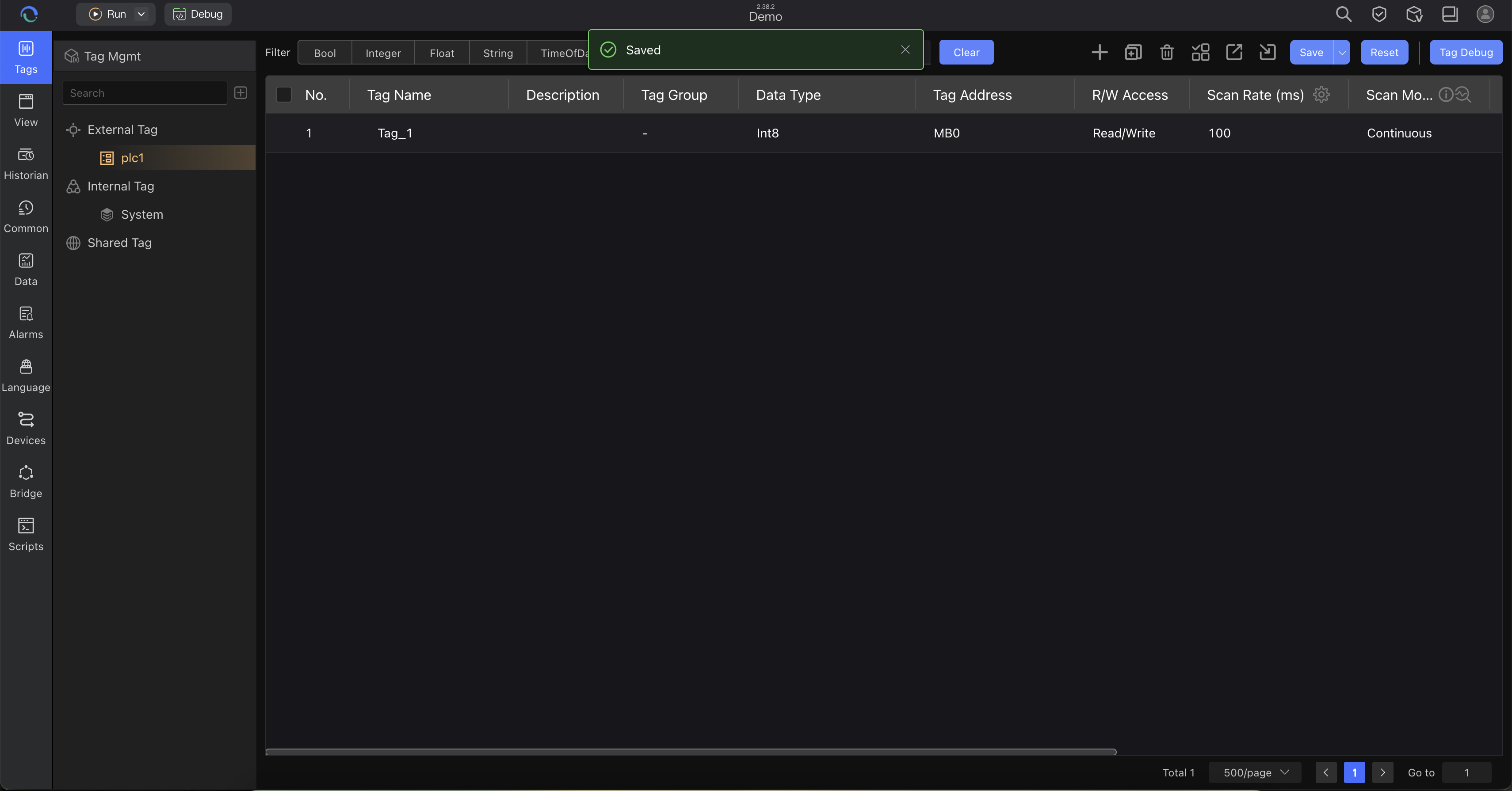
- External Tags: Connect to physical devices (PLCs, sensors, etc.)
- Internal Tags: Used for calculations and logic processing
- System Tags: Predefined system variables
- Shared Tags: Cross-system data sharing
Page View - Design monitoring interfaces

- Drag and drop components to adjust position and size
- Align, distribute, and group components
- Standard components, chart components, control components
Data View - Configure business data tables
- Create custom data tables
- Define fields, trigger conditions, calculation formulas
- Used for production statistics, equipment analysis, batch traceability
Alarm View - Monitor abnormal conditions
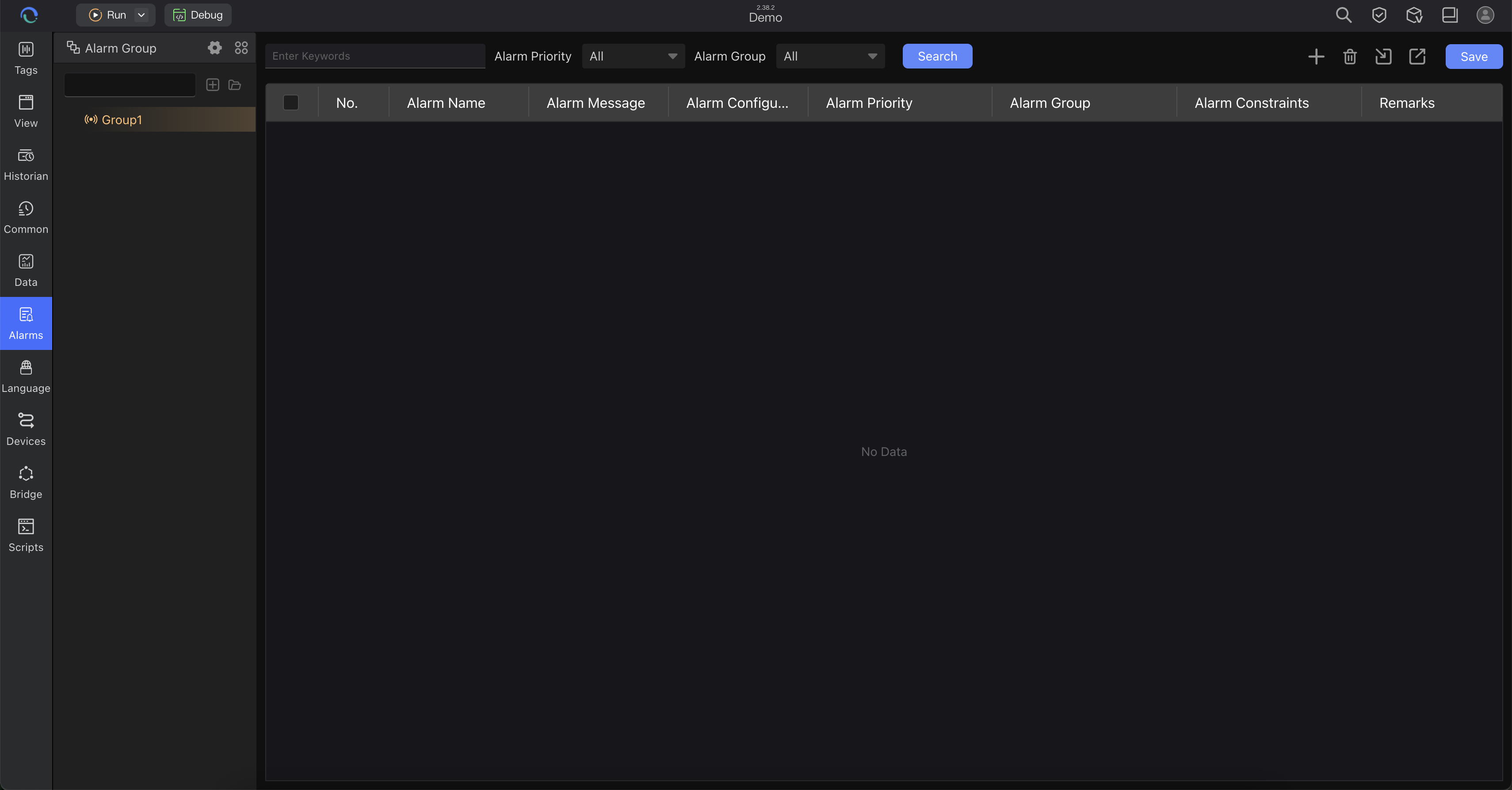
- Create alarm points and set trigger conditions
- Configure alarm levels and notification methods
- Set up interface popups or audio notifications
AI Assistant - AI-driven development
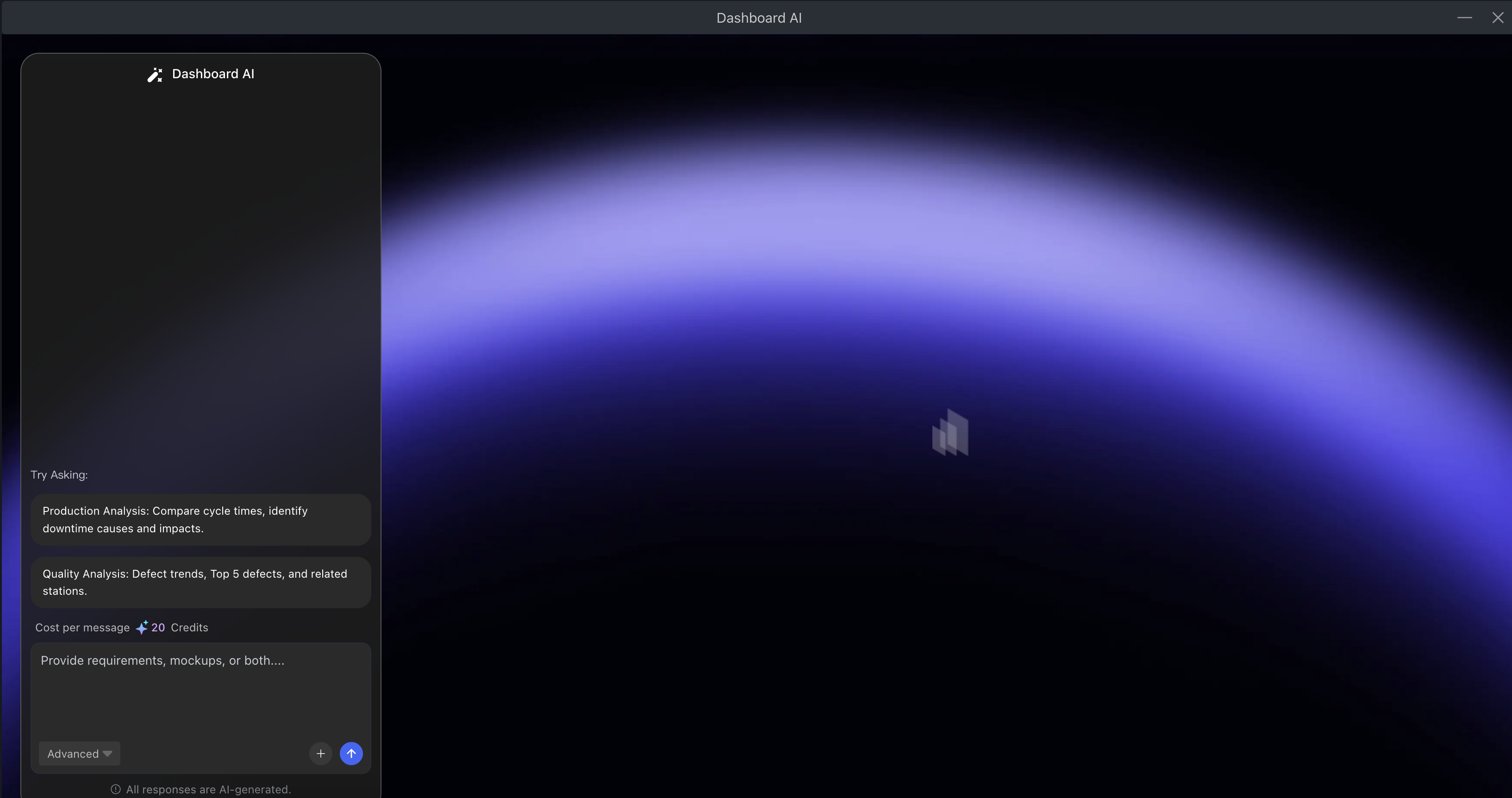
- AI Page Generation: Describe requirements in natural language, generate interfaces in 10-30 seconds
- AI Script Generation: Describe control logic, automatically generate C# code
- AI Smart Binding: Automatically match tags to components
Step 1: Create a Project
Create New Project
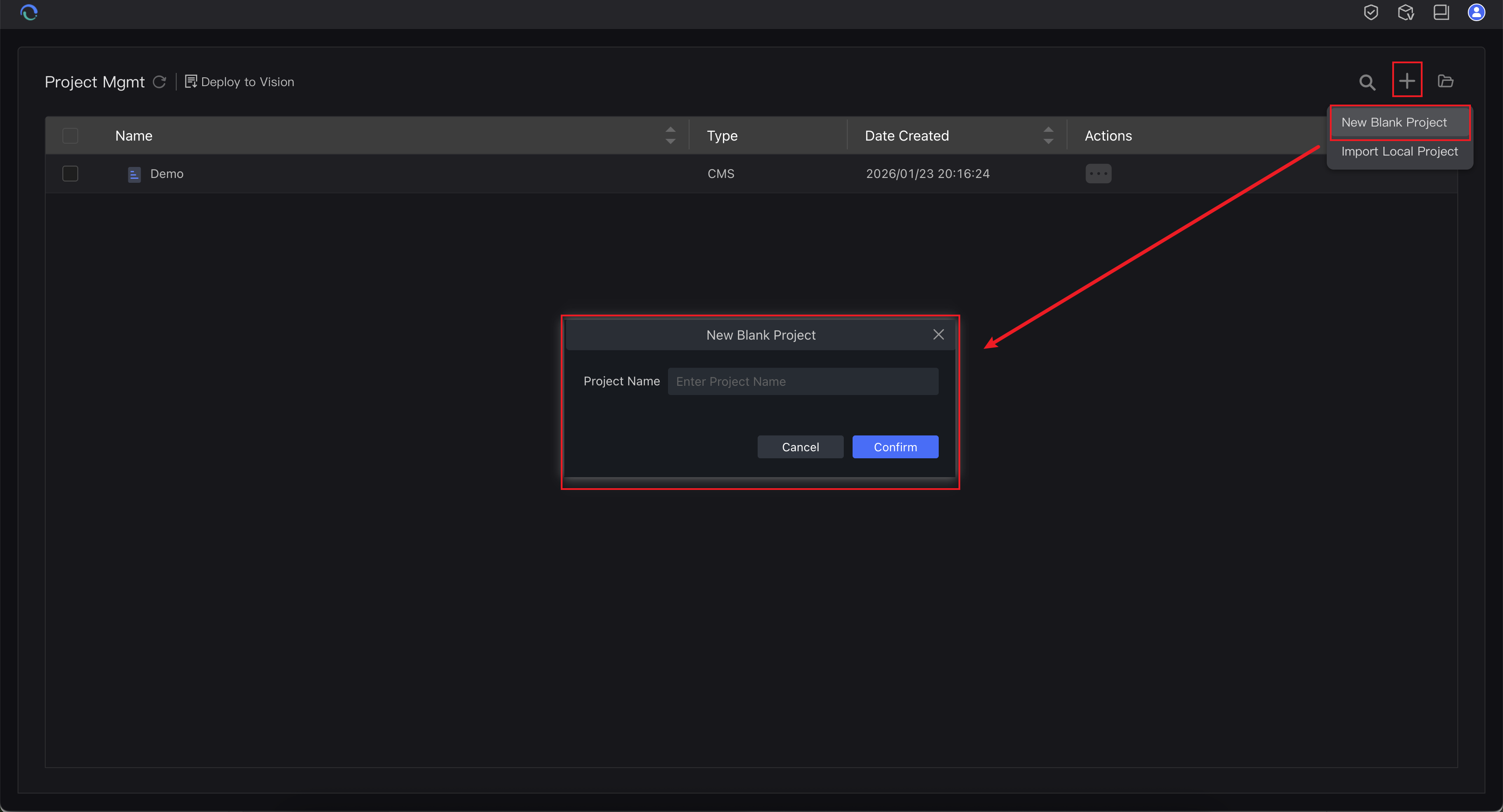
Click "New Project", enter a project name, and confirm.
Enter the Project
Double-click the project record to open it in the Editor.
Step 2: Configure Tags
Add a Channel
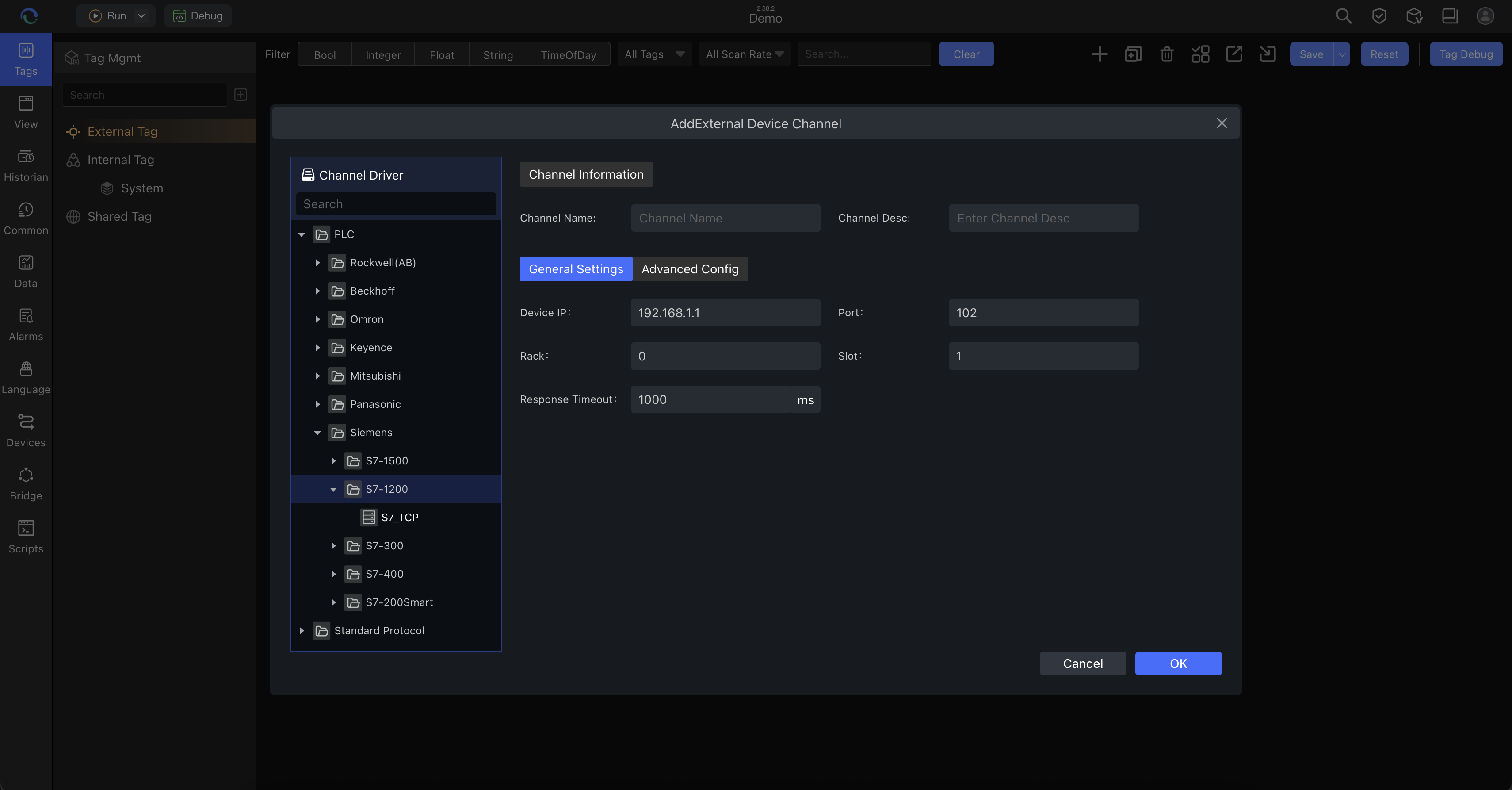
Click "Variable Management" → "Add Channel"
Configure:
- Protocol type (Modbus, S7, OPC UA, etc.)
- Channel name
- Connection parameters (IP address, port)
Add a Variable Group
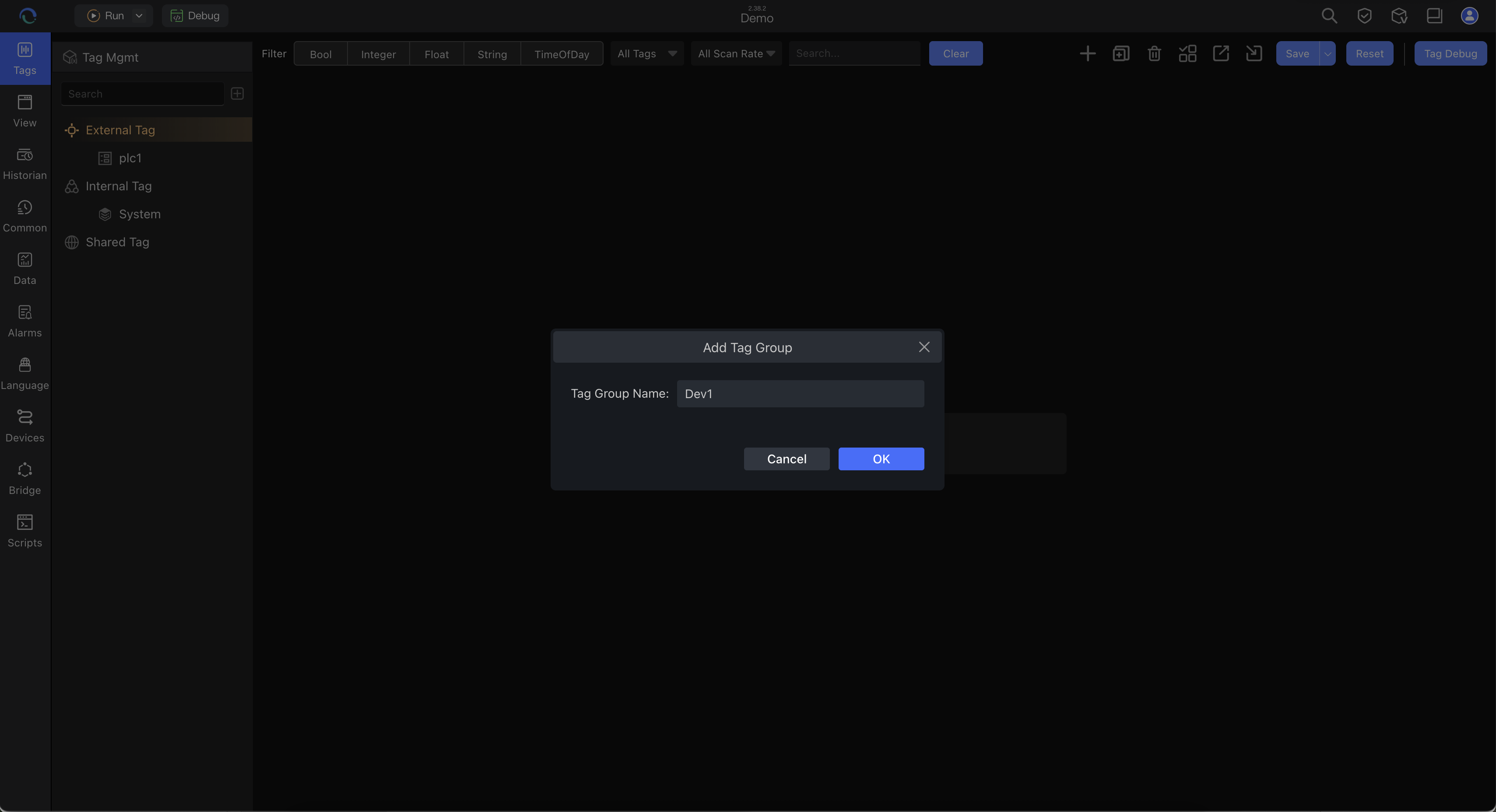
Select the channel → "Add Variable Group" → Enter group name
Add Tags

Select the variable group → "New Variable"
Configure:
- Tag name
- Data type
- Device address
Example:
| Tag Name | Type | Address |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Float | 40001 |
| Pressure | Float | 40002 |
| MotorRunning | Bool | 30001 |
Step 3: Create Pages with AI
AI Page Generation
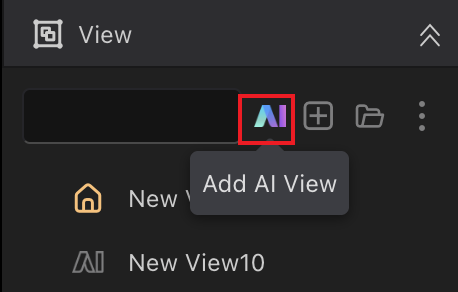
Click "Page Management" → "AI Page Assistant"
Enter your requirements:
Basic example:
Create an equipment monitoring page
Detailed example:
Create a dark tech-style equipment monitoring page with:
- Large temperature gauge (0-100°C)
- Pressure trend chart (last 1 hour)
- Motor running status indicator
- Emergency stop button (red, top-right corner)
Advanced example:
Create an equipment monitoring page with dark blue background, including:
- Left side: Real-time temperature and pressure values
- Right side: Temperature history trend chart
- Bottom: Motor running status indicator
Click "Generate" and wait 10-30 seconds.
AI will automatically:
- Analyze requirements
- Select components
- Create layout
- Apply styling
AI Smart Binding
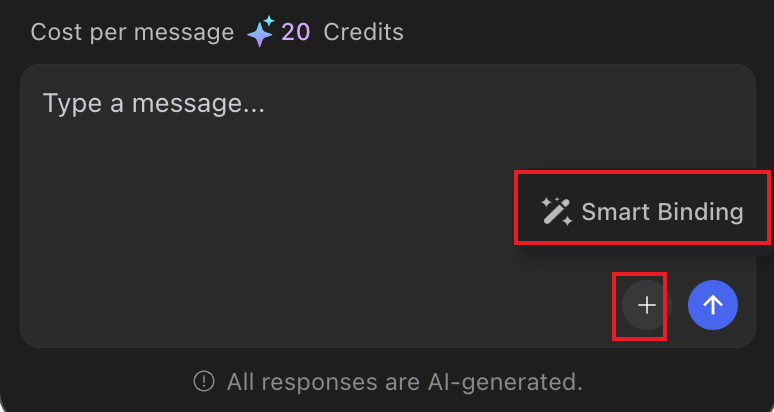
After page generation, click "AI Smart Binding"
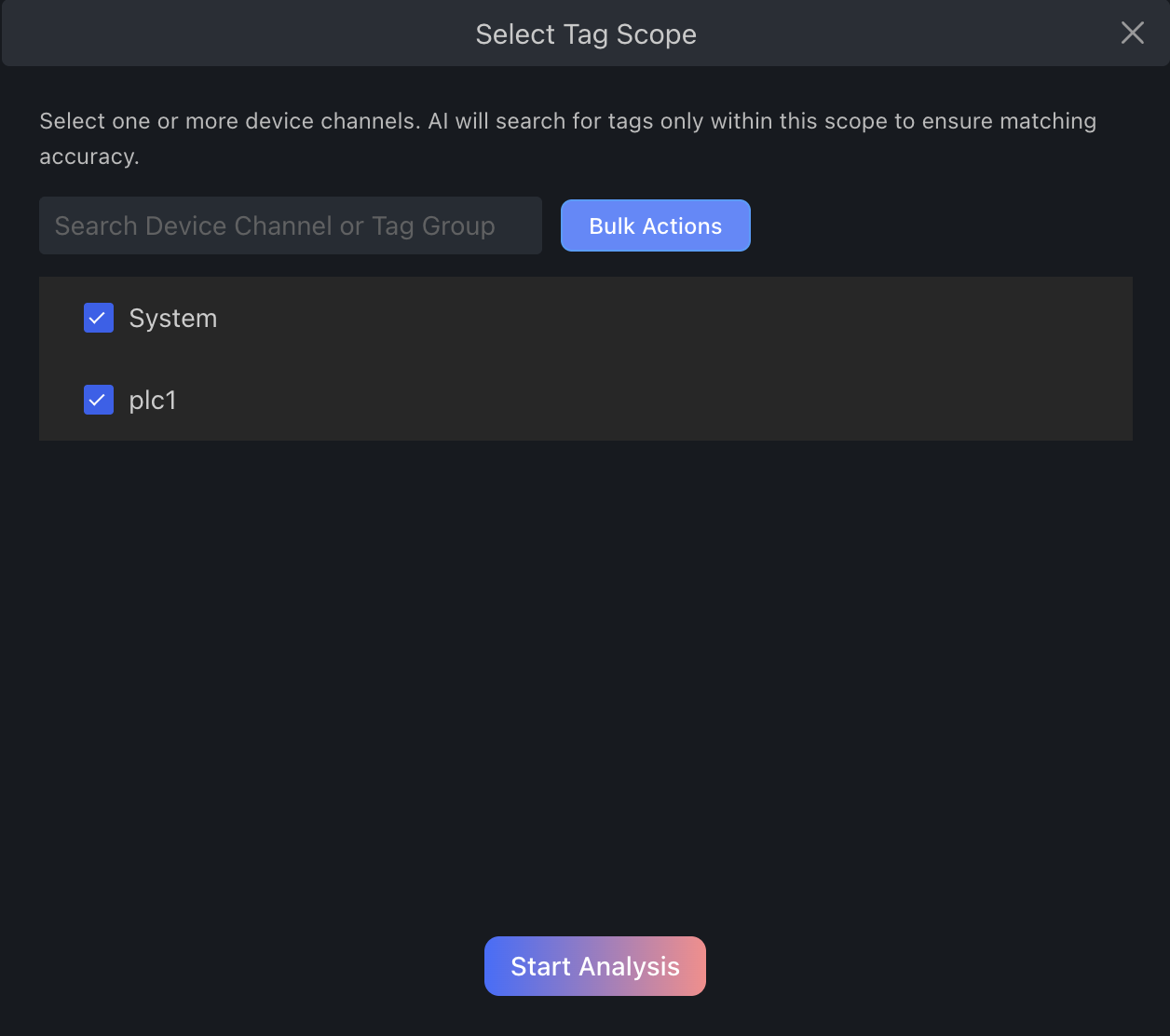
Select the channel or variable group to bind
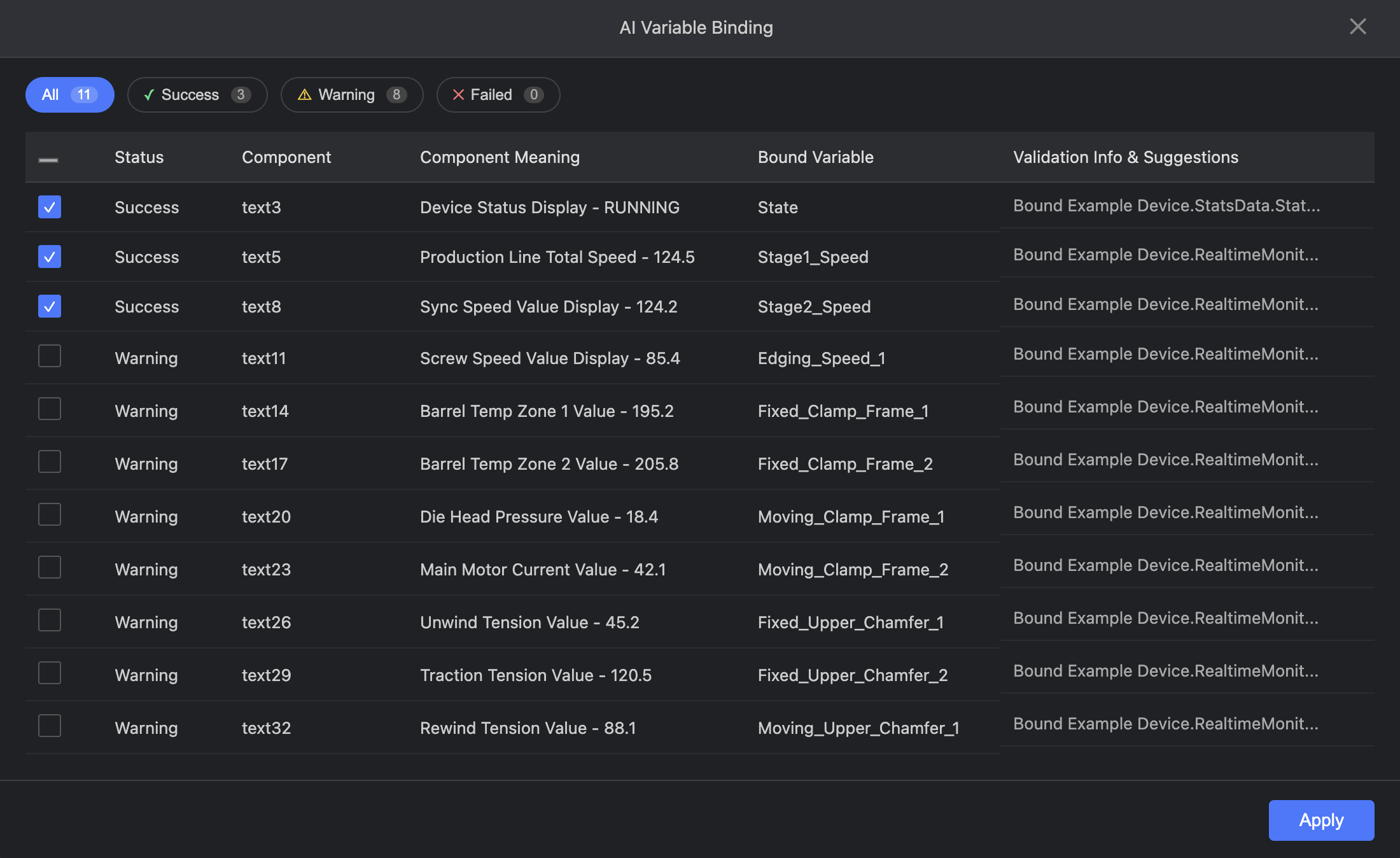
AI automatically analyzes and recommends binding options. Click "Apply" to confirm.
Step 4: Generate Scripts with AI (Optional)
If you need automated control logic:
Open Script Editor
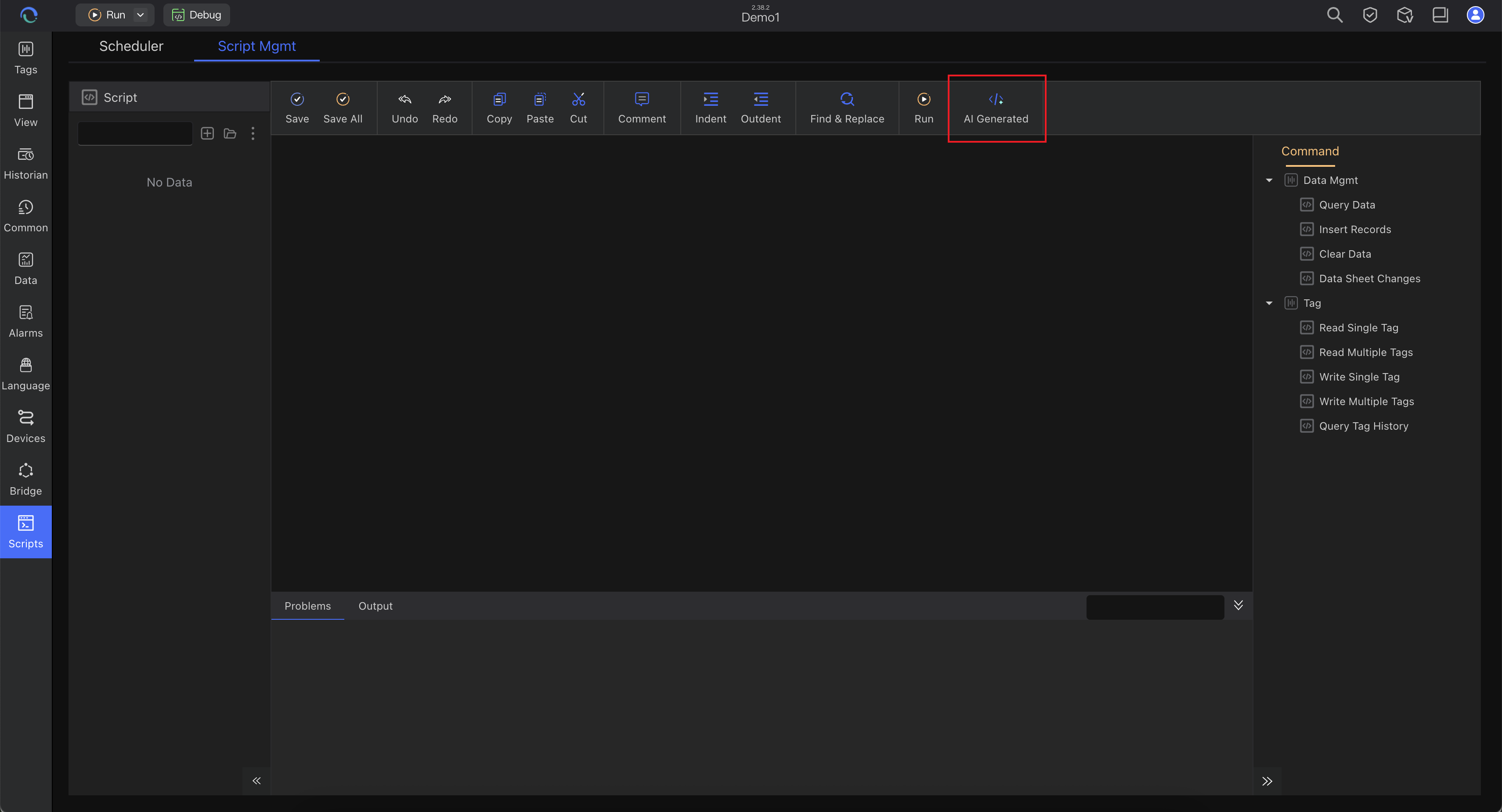
Click "Automation" → "Script Management" → "AI Generate"
Describe the Logic
Enter your requirements, for example:
When temperature exceeds 80 degrees, automatically stop the motor and send an alarm
Generate Script
AI automatically generates C# code:
if (Temperature > 80)
{
MotorRunning = false;
SendAlarm("Temperature too high");
}
Debug and Run
- Test the script
- Review logs
- Optimize logic
Step 5: Run and Test
Start Runtime
Click the "Run" button in the toolbar.
Observe the Results
Watch your project in action:
- Data updates in real-time
- Charts display dynamically
- Test interactive features